News & information
Economics
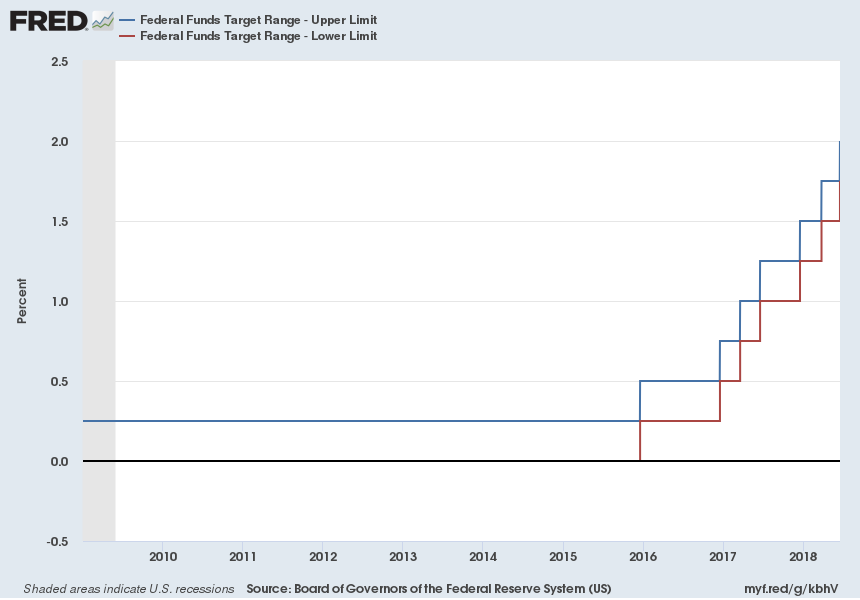
On June 13, 2018, the Federal Reserve raised the target federal funds rate range by another 0.25%, bringing the target range to 1.75%-2.00% (up from 1.50%-1.75%).
During the Great Recession, the Fed’s interest rate target range was lowered all the way to 0.00%-0.25% and remained there for an extended period of time (see chart below).
During a downturn in the economy, lowering interest rates is one of the mechanisms used by the Federal Reserve to try to stimulate economic growth. During the Great Recession, the Fed dramatically lowered interest rates in order to try to boost economic activity. Back in September 2007 the target rate stood at 5.25%. Starting in September 2007, the Federal Reserve began lowering the target, ultimately lowering it 10 times, and ending with a target range of 0.00%-0.25% in December 2008.
In December 2015, as the economy began to show signs of improvement, the Federal Reserve began raising rates. The June 13 increase is the seventh increase since the last recession. The Fed’s full statement about the latest increase can be found here.
One frequent effect of increases in the Fed’s rates is increases in the rates that banks and credit unions use for making loans and paying interest on deposits.
CHART SHOWING THE UPPER AND LOWER FEDERAL FUNDS INTEREST RATE TARGETS
LOWER NOW AT 1.75%, UPPER AT 2.00%